Sommaire Base
Techno Base
Sommaire T Digit
Sommaire P Digit
Sommaire Maths
Sommaire Sites
Ouvrages
Nouveautés
Recherche
- Catégories
- Mathématiques
- Sommaires
- Électronique de Base
- La Loi d'Ohm
- Associations Résistances
- Associations de Piles
- Énergie Électrique
- La Loi de Joule
- Les Condensateurs
- Charge et Décharge
- Électromagnétisme
- Induction Électromagnétique
- Inductance Mutuelle
- Liens entre Atomes
- Structures des Cristaux
- Le Courant Alternatif
- Caractéristiques du C. A.
- Suivez le Sommaire ...
- Technologie de Base
- Théorie des Semi-conducteurs
- Les Diverses Diodes
- Le Transistor Bipolaire
- Régime Saturé ou Bloqué
- Transistors à Effet de Champ
- Fonctions Logiques à Diodes
- Fonctions Logiques à Transistors
- La Fonction OU Câblée
- Logiques à Transistors F.E.T
- Les Circuits Hybrides
- Circuits Intégrés Monolithiques
- Lexique Électronique Numérique
- Théoriques Digitales
- L'information Systèmes Numériques
- Algèbre Logique
- Représentation d'Euler
- Monôme - Polynôme - Karnaugh
- Tableaux de Karnaugh
- Fonctions Nand - Nor - OU Exclusif
- Théorème de DE Morgan
- Méthode de Quine-Mac Cluskey
- Problèmes Résolus - Cluskey
- Systèmes Séquentiels
- Schémas en Logique Séquentielle
- Méthode Matricielle d'Huffman
- Bascule Bistable - RSC - Bascule D
- Diviseur de Fréquence par 2
- Bascule JK Maître Esclave
- Bascules Synchrones "D et JK"
- Suivez le Sommaire pour la suite
- Pratiques Digitales
- Le Simulateur Logique
- Montage du Pupitre Digital
- Montage et Contrôle des Diodes LED
- Contrôle des Transistors
- Examen des Circuits Indicateur à LED
- Circuit Inverseur MM 74C04
- Circuits Intégrés 74C08 et 74C00
- Montage du Groupe d'Interrupteurs
- C.I. OU (74C32) et C.I. NOR (74C02)
- Circuit OU Exclusif MM 74C86
- Bascule Reset - Set (R-S) avec 2 NAND
- Montage des Boutons-Poussoirs
- Bascule R.S. Commande de Validation
- Montage Matrice à Contacts du Digilab
- Contrôle Matrice à 840 Contacts
- Circuit Latch Asynchrones CD 4042
- Bascule D Maître-Esclave - Bascule JK
- Bascule D Utilisé pour la Signalisation
- Suivez le sommaire pour la suite
- Théoriques Computers
- Pratiques Computers
- Synoptique d'un Micro-ordinateur
- Test de Fonctionnement Circuit RESET
- PROM pour Décodage Mémoire
- Vérification du Circuit d'Attente WAIT
- Fonctionnement du Circuit Restart
- Fonctionnement des Circuits Buffers
- Fonctionnement Microprocesseur Z8400
- Montage du Microprocesseur Z8400
- Explication du Microprocesseur Z8400
- Compléments Computers
- Électronique de Base
- Ouvrages et Divers

 Footer
Footer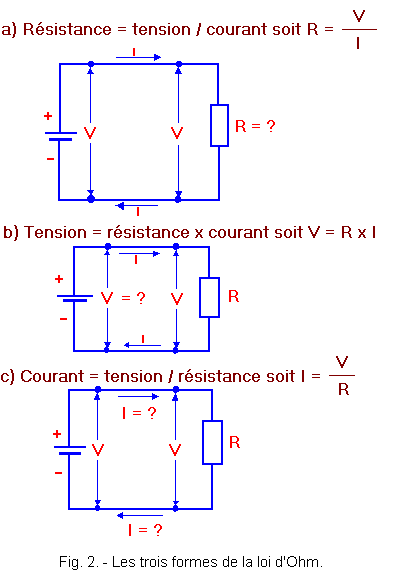
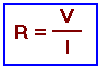
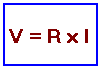
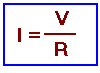
 Click here for the next lesson or in the summary provided for this purpose.
Click here for the next lesson or in the summary provided for this purpose. Next page
Next page 